1. A 55 year old gentleman attends the ED with vertigo. He feels as though the room is spinning and he has intractable vomiting. When you enter the room he is lying still on the bed, every time he moves his head he feels like he is going to fall and vomits.
He has no previous medical illness and until this morning he was well except for a minor upper respiratory tract infection.
- What is the likely diagnosis?
- Give 8 other causes of vertigo.
- You examine the patient and identify no evidence of a central cerebellar lesion. What are 6 signs of cerebellar involvement?
- Name 2 drugs, with doses which you could use for this patient.
Answers:
Answers:
1. What is the likely diagnosis?
- Viral Labyrinthitis
2. Give 8 other causes of vertigo.
- Meniere"s disease (vertigo, tinnitus and deafness)
- Benign positional vertigo (elderly, lasts approximately 2 mins with positional change)
- Otitis media
- Cholesteatoma
- Acoustic neuroma (giddiness more than vertigo, V, VI and VIII cranial nerve palsy, ipsilateral cerebellar signs, loss of corneal reflex)
- CVA
- Trauma
- Wax or foreign body in the ear
- MS
- Alcohol intoxication
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome
3. You examine the patient and identify no evidence of a central cerebellar lesion. What are 6 signs of cerebellar involvement?
The mnemonic DANISH will help to remember them:
- Dysdiadochokinesis/ dysarthria
- Ataxia (gait and posture)
- Nystagmus
- Intention tremor/ past pointing
- Slurred, staccato speech
- Hypotonia/hyperreflexia
4. Name 2 drugs, with doses which you could use for this patient.
- Prochlorperazine: 5 mg PO, 3 mg buccal or 12.5 mg IM
- Betahistine: 8 mg PO
- Cyclizine: 50 mg PO/IM/IV
2. According to ATLS
- List 6 immediate life threatening conditions in chest trauma
- Name 8 potential life threatening chest injuries which might be found on the secondary survey.
- Describe how you would perform pericardiocentesis.
- A 70 Kg patient has just been intubated. At what minute volume would you set the ventilator?
Answers:
Answers:
1. List 6 immediate life threatening conditions in chest trauma
- Tension pneumothorax
- Massive haemothorax
- Cardiac tamponade
- Open pneumothorax
- Flail chest
- Airway obstruction
2. Name 8 potential life threatening chest injuries which might be found on the secondary survey.
- Cardiac contusion
- Lung contusion
- Diaphragmatic injury/rupture
- Simple pneumothorax
- Oesophageal rupture
- Tracheo-bronchial disruption
- Traumatic aortic rupture
- Mediastinal traversing wound
3. Describe how you would perform pericardiocentesis.
- Cardiac monitoring
- 2 cm inferior to xiphisternum
- Aim for left shoulder
- Advance withdrawing syringe and withdraw needle if ST segment elevation on ECG
4. A 70 Kg patient has just been intubated. At what minute volume would you set the ventilator?
Minute volume = Tidal volume x respiratory rate ( 500 ml x 12) = 6L/min
Normal range - 5-8 L/min
More info: Patient.info (pericardiocentesis)
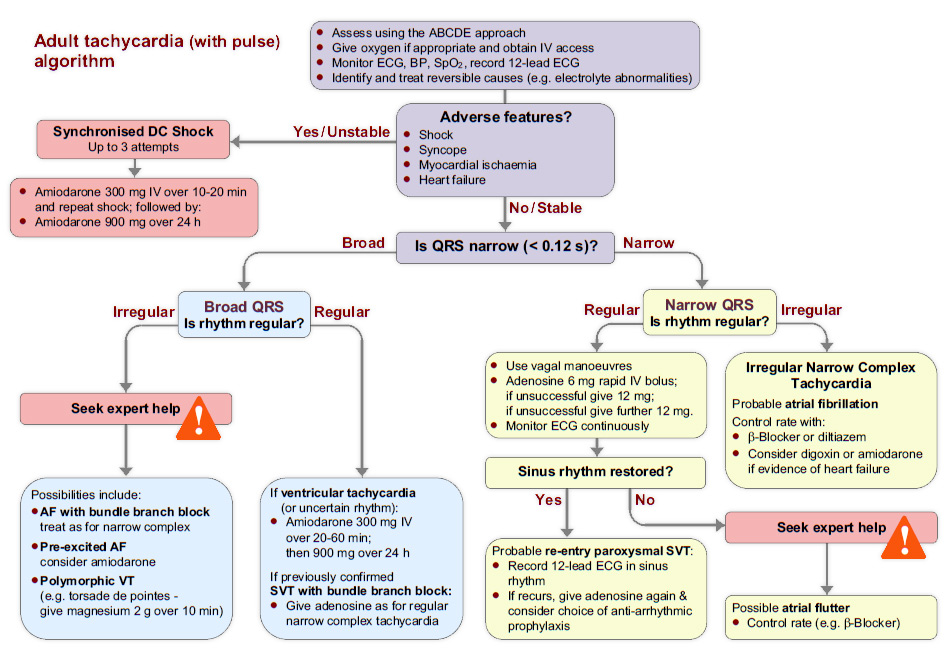
3. A 66 year old man brought to the ED . he has been experiencing palpitations. He is comfortable at rest. His heart rate is 160/min.
- What are 4 signs of instability?
- If a patient displays these signs, what is the immediate course of action? One drug and one non drug with doses as required?
- The ECG shows narrow complex tachycardia which is irregular. What key feature in the history will determine your management?
- Which drug can be used in treatment of atrial fibrillation according to the 2010 resuscitation council guidelines?
- On the bradycardia algorithm, what features indicate increased risk of asystole?
- Outline initial treatment of bradycardia which has failed to respond to an initial dose of atropine. Include doses.
Answers:
Answers:
1. What are 4 signs of instability?
- Shock – hypotension (systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg), pallor, sweating,
cold, clammy extremities, confusion or impaired consciousness. - Syncope – transient loss of consciousness due to global reduction in blood
flow to the brain. - Myocardial ischaemia – typical ischaemic chest pain and/or evidence of
myocardial ischaemia on 12-lead ECG. - Heart failure – pulmonary oedema and/or raised jugular venous pressure
(with or without peripheral oedema and liver enlargement).
2. If a patient displays these signs, what is the immediate course of action? One drug and one non drug with doses as required?
- Synchronised DC shock up to 3 attempts
- Then Amiodarone 300 mg IV over 10-20 minutes followed by 900mg over 24hrs.
ALS Book Says:
- Carry out cardioversion under general anaesthesia or conscious sedation, administered by a healthcare professional competent in the technique being used. Ensure that the defibrillator is set to synchronised mode.
- For a broad-complex tachycardia or atrial fibrillation, start with 120-150 J biphasic shock (200 J monophasic) and increase in increments if this fails.
- Atrial flutter and regular narrow-complex tachycardia will often be terminated by lower energies: start with 70-120 J biphasic (100 J monophasic)".
3. The ECG shows narrow complex tachycardia which is irregular. What key feature in the history will determine your management?
- Onset of arrhythmia <48 hrs. If yes, cardioversion. If no, rate control
4. Which drug can be used in treatment of atrial fibrillation according to the 2010 resuscitation council guidelines?
- Beta Blocker ( Bisoprolol 2.5 to 5 mg PO, Metoprolol 5mg IV)
- Diltiazem or Verapamil if beta blocker in contraindicated or not tolerated.
- Digoxin 500 microgram loading dose ( if evidence of heart failure)
- Amiodarone 300mg over 20-60mins followed by 900mg over 24 hrs.
5. On the bradycardia algorithm, what features indicate increased risk of asystole?
- Recent asystole
- Mobitz II AV block
- Complete heart block with broad QRS
- Ventricular pause > 3 s
6. Outline initial treatment of bradycardia which has failed to respond to an initial dose of atropine. Include doses.
- Atropine 500mg IV to a maximum of 3mg
- Isoprenaline 5 microgram/min
- Adrenaline 2-10 microgram/min
- Transcutaneous pacing
- Alternate drugs: Dopamine, Aminophyline, Glucagon (beta blocker or Ca channel blocker toxicity), Glycopyrrolate
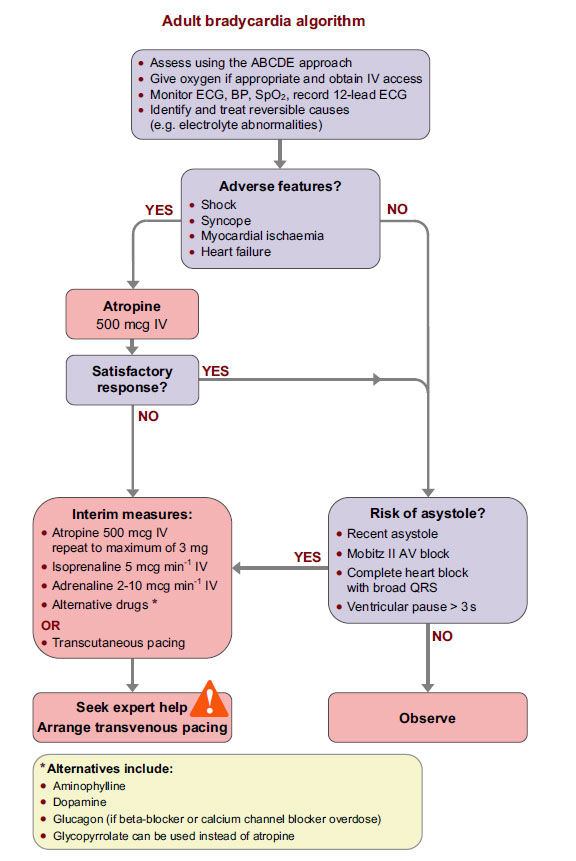
Resus Council Peri-arrest Arrhythmias Guidelines
4. A 35 year old builder attends the ED with a wound on his left thigh which he sustained on some barbed wire yesterday. He is diabetic, on insulin and has no known allergies. He is fully covered for tetanus vaccinations and noticed this morning that his wound, a 2cm superficial wound had become painful and red. The triage nurse marks the 1cm x 2cm area of redness and directs him back to the waiting room. You call him into the cubicle 2 hours later to find him looking unwell. He is pyrexial and looks toxic. The erythema has spread and is now blistered although he says he can"t feel is as much now. His pulse is 110/min and BP of 94/64.
You examine the leg and find it as you see it below.
- What is the likely diagnosis?
- Give 4 features in history and examination would help with the diagnosis.
- What are the usual causative organisms?
- Outline your management of this patient.
Answers:
Answers:
1. What is the likely diagnosis?
- Necrotising fasciitis
2. Give 4 features in history and examination would help with the diagnosis.
- Rapidly spreading erythema
- Dusky purplish discolouration at wound
- Intense and severe pain which may seem out of proportion to any external signs of infection on the skin
- Anaesthesia to affected area at later stage due to nerve damage
- Putrid discharge/bullae/tissue necrosis
- Crepitation felt on tissue due to gas forming infection
- Clinical signs of shock/fever/toxic
3. What are the usual causative organisms?
- Group A haemolytic streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes)
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Clostridium perfringens
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Peptostreptococcus
- Colliforms
- Proteus
- Klebsiella
4. Outline your management of this patient.
- Transfer the patient to resuscitation area
- High flow oxygen with 15L rebreather mask
- IV access and 1L of 0.9% Sodium Chloride stat
- Blood for U&E, FBC, CRP, Culture & Sensitivity, ABG, Urinalysis
- High doses of antibiotics: Benzylpenicillin plus clindamycin plus gentamicin
If penicillin-allergic, meropenem plus clindamycin plus gentamicin - Urgent Plastics/Orthopaedic review
The Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) score can be utilised to risk stratify people having signs of cellulitis to determine the likelihood of necrotising fasciitis being present.
It uses six serologic measures: C-reactive protein, total WBC count, haemoglobin, sodium, creatinine and glucose. A score greater than or equal to 6 indicates that necrotising fasciitis should be seriously considered.
The scoring criteria are as follows:
- CRP (mg/L) ≥150: 4 points
- WBC count (×10³/mm³)
- <15: 0 points
- 15–25: 1 point
- >25: 2 points
- Haemoglobin (g/dL) >13.5: 0 points 11–13.5: 1 point <11: 2 points
- Glucose (mmol/L) >10: 1 point
- Sodium (mmol/L) <135: 2 points
- Creatinine (umol/L) >141: 2 points
- Glucose (mmol/L) >10: 1 point
As per the derivation study of the LRINEC score, a score of ≥ 6 is a reasonable cut-off to rule in necrotising fasciitis, but a LRINEC < 6 does not completely rule out the diagnosis. Diagnoses of severe cellulitis or abscess should also be considered due to similar presentations.
Patient.infoPublic Health England
5. An 8 year old boy attends your emergency department having fallen out of a tree. His only injury is to his right ankle, which is swollen and painful. The X-ray is as shown below.
- Describe the X-ray appearance.
- What is the name of the classification of fracture of this type, and what type is this?
- Describe the other types of fracture in this classification.
- What will be the disposal of this patient and why?
Answers:
Answers:
1. Describe the X-ray appearance.
- Fracture through the epiphysis and epiphyseal plate of the distal tibia.
2. What is the name of the classification of fracture of this type, and what type is this?
- Salter Harris fracture, type 3
3. Describe the other types of fracture in this classification.
- Type I - Slip at the growth plate
- Tupe II - through the metaphysis and growth plate
- Type III - Through epiphysis and growth plate
- Type IV - through both epiphysis and metaphysis
- Type V - crush at the growth plate
4. What will be the disposal of this patient and why?
- Referral to orthopaedics on-call for fixation and there is articular involvement.
6. A 60 year old man presents to your department having tripped over a dog. He has no other injuries except for the fracture of his right femur as shown
- Describe the X-ray.
- What is the diagnosis? What biochemical abnormality would your expect in the blood?
- How would you access the cognitive function of this gentleman.
Answers:
Answers:
1. Describe the X-ray
- Transverse fracture of the femur
- Complete transition
- Proximal displacement of the distal fracture fragment
- Bone shows patchy osteolytic and sclerotic areas
2. What is the diagnosis? What biochemical abnormality would your expect in the blood?
- Paget"s disease
- Increased alkaline phosphatase and rest are normal.
3. How would you access the cognitive function of this gentleman.
| Question | Score |
|---|---|
| What is your age? (1 point) | |
| What is the time to the nearest hour? (1 point) | |
| Give the patient an address, and ask him or her to repeat it at the end of the test. (1 point)e.g. 42 West Street | |
| What is the year? (1 point) | |
| What is the name of the hospital or number of the residence where the patient is situated? (1 point) | |
| Can the patient recognize two persons (the doctor, nurse, home help, etc.)? (1 point) | |
| What is your date of birth? (day and month sufficient) (1 point) | |
| In what year did World War 1 begin? (1 point)(other dates can be used, with a preference for dates some time in the past.) | |
| Name the present monarch/dictator/prime minister/president. (1 point)(Alternatively, the question "When did you come to [this country]? " has been suggested) | |
| Count backwards from 20 down to 1. (1 point) |
A score of 7-8 or less suggests cognitive impairment at the time of testing, although further and more formal tests are necessary to confirm a diagnosis of dementia, delirium or other causes of cognitive impairment.
More info on Paget"s Disease
7. A 75 year old man presents with 5 weeks history of back pain and gradual loss of mobility. His daughter says that whilst he used to be completely independent and walk several miles a day, he now needs help around the house and his exercise tolerance is reduced to 50m before he becomes short of breath. Over the past 24 hrs he has become drowsy.
FBC:
- HB 82mg/dl
- Platelet 45 x 109/L
- WCC 4.3 x 109/L
BCP:
- Na 145 mmol/L
- K 5.5 mmol/L
- Urea 18.7 mmol/L
- Creatinine 324 μmol/L
- Give 2 possible cause of his drowsiness.
- What is the cause of his decreased exercise tolerance?
- What is the unifying diagnosis?
- Name one blood and one non-blood test you could do to confirm the overall diagnosis, and the expected results.
- Name one further biochemical test you would like to perform urgently?
Answers:
Answers:
1.Give 2 possible cause of his drowsiness.
- Renal failure
- Hypercalcaemia
2. What is the cause of his decreased exercise tolerance?
- Anaemia
3. What is the unifying diagnosis?
- Multiple myeloma
4. Name one blood and one non-blood test you could do to confirm the overall diagnosis, and the expected results.
- Urine - Benz Jones protein
- Blood - Plasma electrophoresis - monoclonal bands
5. Name one further biochemical test you would like to perform urgently?
- Serum calcium
In 2003, the International Myeloma Working Group agreed on diagnostic criteria for symptomatic myeloma which was subsequently updated in 2009
Symptomatic myeloma:
- Clonal plasma cells >10% on bone marrow biopsy or (in any quantity) in a biopsy from other tissues (plasmacytoma)
- A monoclonal protein (paraprotein) in either serum or urine (except in cases of true non-secretory myeloma)
- Evidence of end-organ damage felt related to the plasma cell disorder (commonly referred to by the acronym "CRAB"):
- HyperCalcemia (corrected calcium >2.75 mmol/L)
- Renal insufficiency attributable to myeloma
- Anemia (hemoglobin <10 g/dL)
- Bone lesions (lytic lesions or osteoporosis with compression fractures)
More info about Multiple Myeloma
8. A man is brought to the ED following a gas explosion in a house. He has 30% burns to arm and trunk, which are circumferential, and burns to his neck and right side of the face and mouth. He looks about 70 kg. His breathing is noisy and his respiratory rate is 40/min wit poor air entry. His pulse is 120/min and his BP os 90/50. His GCS is 10/15.
- Outline 8 steps in his initial management (and investigations)
- Calculate his fluid requirements. How much do you give in 24hrs, over what period do you divide the fluid and what type of fluid do you give?
- He is intubated and the anaesthetist says she is finding it increasingly difficult to bag the patient. What one thing you can do to improve his breathing?
- Give 4 complication of electrical injury.
Answers:
Answers:
1. Outline 8 steps in his initial management (and investigations)
- Oxygen 15L/min using non-rebreather mask
- C Spine control with collar
- Call senior anaesthetist
- Get the emergency surgical airway equipment ready
- Monitoring: SpO2, 3 lead ECG, BP
- Intubate with RSI (care using Sux)
- IV fluid resuscitation
- IV analgesia using opioids
- Blood for FBC, U&E, CK, ABG, Group & Save/Cross Match
- Trauma CT if appropriate, else chest and pelvis X-ray
- Urethral catheter
- Tetanus prophylaxis
- Referral to regional burns unit
2. Calculate his fluid requirements. How much do you give in 24hrs, over what period do you divide the fluid and what type of fluid do you give?
- Parkland"s formula: %of burn x body weight x 2-4ml /24hrs
- 30 x 70 x 4ml = 8400ml in 24hrs
- Give half (4200ml) over first 8 hrs (since incident) and rest over next 16 hrs.
- 525ml of crystalloids/hr for first 8 hrs
3. He is intubated and the anaesthetist says she is finding it increasingly difficult to bag the patient. What one thing you can do to improve his breathing?
- Escharotomy of chest
4. Give 4 complication of electrical injury.
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Dislocation or fracture
- Renal failure due to myoglobinuria
- Compartment syndrome
- Neurological deficit e.g. coma, seizures, headache, transient paralysis
- Ophthalmic e.g. cataracts and glaucoma
- Full thickness burns
9. A 35 year old female brought to your ED by her family who say that she has suddenly started behaving strangely. She has had low in mood for a few days but today has become completely catatonic. Her eyes are open but she will not respond.
No psychaitric history. Gravida 4, para 2. Recent joint and muscle pains.
Her airway, breathing and circulation are normal.
Rest of examination unremarkable. Temp 38.7
Bloods:
- Na 140, K 4.0, Urea 12.0, Creatinine 107, CRP 8, ESR 120
- Hb 87, WCC 2.3, Plt 350
- What features would you look for in the history that would favour an organic from a psychiatric cause?
- What features would you look for in your examination of the patient?
- What is you differential diagnosis?
- What would be your next 2 investigations?
- If these are normal, what would be your next investigation?
Answers:
Answers:
1. What features would you look for in the history that would favour an organic from a psychiatric cause?
- Disorientation
- Impairment of memory, judgment, and intellectual function
- Anxious
- Irritable
- Agitation
- Drug history
- No previous psychiatric involvement
2. What features would you look for in your examination of the patient?
- Features of sepsis
- Neck stiffness
- Skin rash suggesting meningitis
3. What is you differential diagnosis?
- SLE
- Encephalitis
4. What would be your next 2 investigations?
- CT brain
- Lumber puncture and CSF analysis
5. If these are normal, what would be your next investigation?
- Anti Nuclear antibody - SLE
10. A 25 year old women presents to the ED with lower abdominal pain and vaginal discharge. She has a tender lower abdomen with no signs of peritonism.
Bloods: Hb 150, WCC 12, CRP 20, MSU - negative
- Give four differential diagnosis.
- Give three diagnostic criteria for PID
- What are the indication for admission?
Answers:
Answers:
1. Give four differential diagnosis.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Appendicitis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- UTI
2. Give three diagnostic criteria for PID
- Lower abdominal tenderness which is usually bilateral
- Adnexal tenderness on bimanual vaginal examination
- Cervical motion tenderness on bimanual vaginal examination
- Fever (>38°C)
3. What are the indication for admission?
- A surgical emergency cannot be excluded
- Lack of response to oral therapy
- Clinically severe disease
- Presence of a tuboovarian abcess
- Intolerance to oral therapy
- Pregnancy
The following features are suggestive of a diagnosis of PID
Symptoms
- lower abdominal pain which is typically bilateral
- deep dyspareunia
- abnormal vaginal bleeding, including post coital, inter-menstrual and menorrhagia
- abnormal vaginal or cervical discharge which is often purulent
Signs
- lower abdominal tenderness which is usually bilateral
- adnexal tenderness on bimanual vaginal examination
- cervical motion tenderness on bimanual vaginal examination
- fever (>38°C)
Causative organisms:
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Gardnerella vaginalis
- Anaerobes
Treatment
Outpatient
- i.m. ceftriaxone 500mg single dose followed by oral doxycycline 100mg twice daily plus metronidazole 400mg twice daily for 14 days or
- Oral ofloxacin 400mg twice daily plus oral metronidazole 400mg twice daily for 14 days
Inpatient
- i.v. ceftriaxone 2g daily plus i.v. doxycycline 100mg twice daily (oral doxycycline may be used if tolerated) followed by oral doxycycline 100mg twice daily plus oral metronidazole 400mg twice daily for a total of 14 days or
- i.v. clindamycin 900mg 3 times daily plus i.v. gentamicin (2mg/kg loading dose) followed by 1.5mg/kg 3 times daily [a single daily dose of 7mg/kg may be substituted]) followed by either oral clindamycin 450mg 4 times daily or oral doxycycline 100mg twice daily plus oral metronidazole 400mg twice daily to complete 14 days
Reference: bashh.org
11. A 15 yr old farmers daughter presented with a 5 day history of RUQ pain. On examination she is pyrexial at 38.4°C. She looks unwell and jaundiced. Her parents say she has been unhappy at home for the past month, since they came back from holiday in Egypt.
Investigations:
FBC: HB 80mg/dl, WCC 18.8, Plt 140, Reticulocyte count 20%, No fragmented RBC seen, PT 36 (control 12), APTT 59 (control 45)
U&E: Na 136, K 4.9, U 26, Cr 400, Bil 50, AST 900, ALP 300, Alb 33
Serology: HepB sAg - absent, HCV Ab - absent, CMV serology - absent, Monospot - negative
- Suggest 2 possible infective causes.
- Suggest 2 possible non-infective causes.
- Give 2 possible causes of anaemia
- If fragmented RBC"s had been seen, what would this suggest?
Answers:
Answers:
1. Suggest 2 possible infective causes.
- Hepatitis A
- Leptospirosis (Weil"s disease)
2. Suggest 2 possible non-infective causes.
- Paracetamol overdose
- Iron overdose
3. Give 2 possible causes of anaemia
- Haemolysis
- Bleeding secondary to impaired coagulation
4. If fragmented RBC"s had been seen, what would this suggest?
- Haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS)
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS) is a triad of:
- Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia (Coombs" test negative).
- Thrombocytopenia.
- Acute kidney injury (acute renal failure).
HUS usually arises within 14 days after the onset of diarrhoea due to VTEC (verotoxin-producing E. coli) infection (the mean period reported in the UK is 6-8 days but this interval may be more prolonged)
Further read: HUS
12. A 75 yr old female was brought to ED after being found on the floor by the home help. She complained of frequent dizzy spells, particularly on standing. She had several falls at home and 2 hospital admissions, and was increasingly dependant on social services. She also complaining of lethargy, hoarse voice, intermittent confusion and weight gain of 7kg in the past 7 months. PMH OA. Drug History: Paracetamol
O/E: She is pale and frail, HR 60/min, BP 200/60 lying and 90/50 standing. JVP not raised. Slightly displaced apex beat. Soft 1st and 2nd HS. Chest, abdomen and neuro examinations were normal.
FBC: Hb 100, WCC 6, Plt 149
BCP: Na 118, K 5.3, U 3.0, Cr 69, LFT - normal, ECG - normal, CXR - enlarged heart
- What is the cause of her falls?
- What condition could be causing this?
- What test could be used to confirm this?
- What other biochemical abnormality do the symptoms suggest?
- Name two tests, one to confirm the diagnosis, and one to investigate an important biochemical side effect of this condition.
Answers:
Answers:
1. What is the cause of her falls?
- Postural hypotension
2. What condition could be causing this?
- Addison"s disease
3. What test could be used to confirm this?
- Short synacthen test
4. What other biochemical abnormality do the symptoms suggest?
- Hypothyroidism
5. Name two tests, one to confirm the diagnosis, and one to investigate an important biochemical side effect of this condition.
- Thyroid function test
- Random lipid profile
Routine laboratory investigations may show the following in Addisons Disease:
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypoglycemia, (worse in children due to loss of glucocorticoid"s glucogenic effects)
- Hyponatremia, due to loss of production of the hormone aldosterone, to the kidney"s inability to excrete free water in the absence of sufficient cortisol, and also the effect of corticotropin-releasing hormone to stimulate secretion of ADH.
- Hyperkalemia, due to loss of production of the hormone aldosterone.
- Eosinophilia and lymphocytosis
- Metabolic acidosis, also is due to loss of the hormone aldosterone because sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule is linked with acid/hydrogen ion (H+) secretion. Low levels of aldosterone stimulation of the renal distal tubule leads to sodium wasting in the urine and H+ retention in the serum.
The short synachten test compares blood cortisol levels before and after 250 micrograms of tetracosactide (intramuscular or intravenous) is given. If, one hour later, plasma cortisol exceeds 170 nmol/l and has risen by at least 330 nmol/l to at least 690 nmol/l, adrenal failure is excluded. If the short test is abnormal, the long test is used to differentiate between primary adrenal insufficiency and secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
The long test uses 1 mg tetracosactide (intramuscular). Blood is taken 1, 4, 8, and 24 hr later. Normal plasma cortisol level should reach 1000 nmol/l by 4 hr. In primary Addison"s disease, the cortisol level is reduced at all stages, whereas in secondary corticoadrenal insufficiency, a delayed but normal response is seen.
It should be noted that dexamethasone does not cross-react with Synachten test result and can be administered concomitantly during testing.
SAQ - Practice Paper 3