Question 1:
A 66 year old male presents to ED with chest pain. His pulse 100, BP 90/58.

The CT1 doctor has commenced Oxygen and given the patient 3 mg buccal nitrate
- What does the ECG show? What is the diagnosis?
- What would you tell the SHO to do?
- List 5 treatment options.
- Which vessel is involved?
Answer
Answer
A 66 year old male presents to ED with chest pain. P100, BP 90/58.
The SHO has commenced Oxygen and given the patient 3mg buccal nitrate
1. What does the ECG show? What is the diagnosis?
- Rate 60bpm
- ST elevation II, III, AVF
- ST depression aVL, V1-V6.
- Inf MI with RV involvement.
2. What would you tell the CT1 to do?
- Remove nitrate
- Lie patient flat.
3. List 5 treatment options.
- Aspirin 300mg
- IV fluid bolus 100-200mg to increase filling pressure RV
- IV opiate plus anti emetic eg metoclopramide
- Depending upon local policy –thrombolysis or PCI.
4. Which vessel is involved?
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA)


Question 2:
A 61 year old man presents with central chest pain, he is a NIDDM.
He has a troponin I level of <5.

- Describe the ECG
- Give 5 components of the TIMI score.
- The patient has received aspirin, nitrates and analgesia, give 3 further pharmacological interventions as the patient has ongoing pain.
Answer
Answer
A 61 year old man presents with central chest pain, he is a NIDDM.
He has a troponin I level of <5.
1. Describe the ECG
- Sinus rhythm
- Rate 75bpm
- Marked ST depression V3-V6
2. Give 5 components of the TIMI score.
- Age >60
- Elevated cardiac marker
- Previous stenosis> 50%
- ST depression on presenting ECG
- Three or more risk factors for coronary artery disease eg Cig, FH, hypertension, hypercholesterolaemia, DM
- Aspirin use in preceding 7 days
The patient has received aspirin, nitrates and analgesia, give 3 further pharmacological interventions as the patient has ongoing pain.
- IV opiate eg DM 5mg IV
- IV nitrate infusion titrated to symptoms/BP
- LMWH eg enoxaparin 1mg/kg
- Beta blocker eg Atenolol 5mg
- Clopidogrel 300mg
- Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor.
Question 3:
56-year-old man presents with a 2 hour history of severe central chest pain, vomiting and sweating +++.
On arrival in ED he is seen by a junior doctor who gives Oxygen, gets IV access and an ECG and gives a 5mb buccal tablet and diamorphine 2mg with anti-emetic.
His observations on arrival were P=95/min BP= 169/105.
The doctor comes to ask for your help, as the patient is now more sweaty and confused with a BP 85/45.

- Describe the ECG.
- What is your diagnosis?
- Why is the patient hypotensive?
- Which coronary vessel is likely to be involved?
- How would you manage this patient?
- What does the following ECG show?

Answer
Answer
56-year-old man presents with a 2 hour history of severe central chest pain, vomiting and sweating +++.
On arrival in ED he is seen by a junior doctor who gives Oxygen, gets IV access and an ECG and gives a 5mb buccal tablet and diamorphine 2mg with anti-emetic.
His observations on arrival were P=95/min BP= 169/105.
The doctor comes to ask for your help, as the patient is now more sweaty and confused with a BP 85/45.
1. Describe the ECG.
- 1st degree heart block
- ST elevation II,III,aVF, ST depression I, aVL, T inversion V1-V4
2. What is your diagnosis?
- Inferior MI with involvement of RV
3. Why is the patient hypotensive?
- Right ventricular infarction, and buccal nitrate tablet
4. Which coronary vessel is likely to be involved?
- Right Coronary Artery
5. How would you manage this patient?
- Give gentle fluid bolus 100-200ml saline and reassess BP
- Depending upon local hospital protocol give thrombolysis or refer for PCI
6. What does the following ECG show?
- Complete heart block
Question 4:
A 21 year old male presents with palpitations. He brings with him a copy of his ECG recorded by his General Practitioner 3 weeks ago (A).At present he is on a cardiac monitor with P= 180, BP 100/60, Alert and orientated but feeling dizzy.
A
 B. The 12 lead taken in ED shows
B. The 12 lead taken in ED shows

- Describe ECG A.
- Outline treatment plan for current attendance
- Amiodarone is a commonly used antiarrhythmic agent. What are its :
- mode of action (1)
- 4 common side effects (1/2 each)
- 1 contraindication (1)
Answer
Answer
A 21 year old male presents with palpitations. He brings with him a copy of his ECG recorded by his General Practitioner 3 weeks ago (A).At present he is on a cardiac monitor with P= 180, BP 100/60, Alert and orientated but feeling dizzy.
1. Describe ECG A.
- Sinus
- Rate 80bpm
- Short PR interval
- Widening of QRS with delta waves
- LVH
2. Outline treatment plan for current attendance
- Oxygen, cardiac monitoring, IVA
- Vagal manouvers
- Adenosine if it is SVT
- If in AF, DC cardioversion or IV Amiodarone, early liaison with cardiology.
3. Amiodarone is a commonly used antiarrhythmic agent,, what are its :
Mode of action
- Class III antiarythmic acts to prolong duration of action potential, also acts on fast NA channels and B adrenergic receptors.
4 common side effects
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Skin discolouration
- Corneal microdeposits
- Lung fibrosis
- Hepatic toxicity
- Peripheral neuropathy
One contraindication
- Pregnancy/breast feeding
- 2nd degree/3rd degree heart block
- Iodine allergy
Question 5:
A 74 year old female presents after waking at 5 am with sudden severe dyspnoea. SpO2 86% OA, afebrile. CXR shown below.

- List 4 features shown on CXR
- What is the diagnosis?
- Explain by drawing or words Starling’s curve and how it might differ in this patient
- Give 3 drugs with doses and routes you would use in this patient
- What is the stimulus for releases of ANP and by what mechanism does it act?
Answer
Answer
A 74 year old female presents after waking at 5am with sudden severe dyspnoea. SpO2 86% OA, afebrile. CXR shown below.
1. List 4 features shown on CXR
- Cardiomegaly
- Fluid in horizontal fissure
- Kerley B lines
- Alveolar hilar shadowing
- Bilateral pleural effusion
2. What is the diagnosis?
- Acute pulmonary oedema.
3. Explain by drawing or words Starling’s curve and how it might differ in this patient

The Frank–Starling law of the heart states that the stroke volume of the heart increases in response to an increase in the volume of blood filling the heart (the end diastolic volume) when all other factors remain constant. The increased volume of blood stretches the ventricular wall, causing cardiac muscle to contract more forcefully (the so-called Frank–Starling mechanisms)
Contractility can increase or decrease SV independent of LVEDP
4. Give 3 drugs with doses and routes you would use in this patient
- High flow Oxygen, 15L via non –rebreather mask
- Nitrates, IV GTN, 50mg in 50ml saline starting at 0.6mg/hr, and titrated to response and BP.
- Opiates - 2.5-5mg IV diamorphine
- Frusemide 50mg IV
5. What is the stimulus for releases of ANP and by what mechanism does it act?
- ANP is released by excess volume and hence stretch of atria. Acts as antagonist to rennin-angiotensin system, increases renal sodium excretion so increasing naturesis
Question 6:
A 75 year old female presents with recurrent syncope.

- Describe the ECG
- List 4 common potential causes
- The patient drops her BP to 70/30. How would you manage the patient?
Answer
Answer
A 75 year old female presents with recurrent syncope.
1. Describe the ECG
- Broad complex tachycardia
- Capture beats
- Fusion beats
2. List 4 common potential causes
- Metabolic abnormalities eg hyperkalaemia
- Drugs eg. TCA, quinidine, procainamide, digoxin
- Long QT syndrome (congenital, acquired)
- MI/IHD
3. The patient drops her BP to 70/30. How would you manage the patient?
- Oxygen
- IVA
- If conscious sedate with IV midazolam before DC cardioversion, 150J biphasic, 200J monophasic.
- Cardiology review and CCU admission.
Question 7:
45 year old male presents with 2 hour history of central crushing chest pain, sweaty and vomited twice. No PMH. On Oxygen, ongoing pain.

- What does the ECG show?
- What is the diagnosis? What blood vessel is involved?
- Give 4 management steps
- Using the same ECG, the patient is a 76 year old man. PMH MI 3/12, 30min pain, now resolved, normal observations. Give 4 management steps
Answer
Answer
45 year old male presents with 2 hour history of central crushing chest pain, sweaty and vomited twice. No PMH. On Oxygen, ongoing pain.
1. What does the ECG show?
- Sinus rhythm
- LBBB
2. What is the diagnosis? What blood vessel is involved?
Acute MI, cause by proximal occlusion of LAD.
3. Give 4 management steps
- Aspirin300mg
- Nitrate, 5mg sublingual or IV
- Diamorphine 5mg IV ( Morphine if Diamorphine is not available)
- PCI or thrombolysis depending upon local protocol.
4. Using the same ECG, the patient is a 76 year old man. PMH MI 3/12, 30min pain, now resolved, normal observations. Give 4 management steps
- Aspirin 300mg PO
- Clopidogrel 300mg PO
- Enoxaparin 1mg/kg (or Dalteparin) SC
- Request old ECG
- Refer for admission
Question 8:
75 year old male presents having collapse, paramedics had difficult detecting pulse.
1. Describe the ECG, what is the diagnosis?

The patient has another ‘funny do’ in the ED, repeat ECG is below.
 2. Describe the ECG
2. Describe the ECG
3. How would you manage this patient?
4. What asystolic rhythm might he develop?
Answer
Answer
75 year old male presents having collapse, paramedics had difficult detecting pulse.
1. Describe the ECG, what is the diagnosis?
- Sinus rhythm
- Rate 75bpm
- Left axis deviation (LAD) p
- Prolonged P-R interval
- RBBB
- Incomplete Trifascicular block (1st degree AV block, RBBB, LAD)
The patient has another ‘funny do’ in the ED, repeat ECG is below.
2. Describe the ECG.
- Complete trifascicular block (LAD, RBBB and Third degree heart block)
- Bradycardia, vent rate of approx 30bpm
- No relationship P and QRS
3. How would you manage this patient?
- Oxygen
- IVA
- Atropine 0.5 mg IV whilst setting up transcutaneous pacing, adrenaline 2-10ug/kg/min
- Cardiology review for pacemaker.
4. What asystolic rhythm might he develop?
- P wave asystole, ie. ventricular standstill
Question 9:
A 30 year old female presents with SOB and dizziness. Her blood pressure 80/40 mm Hg.

1. What is the diagnosis?
2. How would you manage this patient?
Answer
Answer
A 30 year old female presents with SOB and dizziness. Her blood pressure 80/40 mm Hg.
1. What is the diagnosis?
- Narrow complex tachycardia with rate 150bpm (Supra Ventricular Tachycardia)
2. How would you manage this patient?
- Oxygen
- IV access and fluid bolus
- Sedate with IV midazolam (or Propofol) if conscious prior to DC cardioversion 150J biphasic, 200J monophasic
- Amiodarone (if cardioversion unsuccessful) 300mg over 10-20 mins followed by repeat cardioversion. Remaining 900mg over 24 hours.
- Cardiology review
Question 10:
A 39 year old female presents with palpitations and collapse. Her BP on arrival is 95/55.
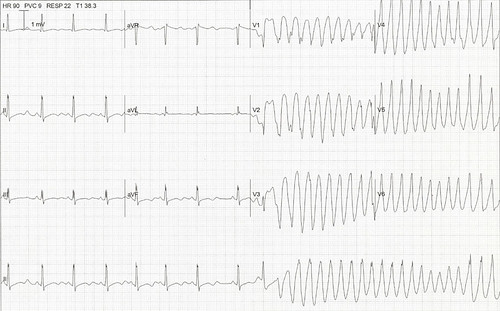 1. Describe the ECG, what is the diagnosis?
1. Describe the ECG, what is the diagnosis?
2. Give 3 possible causes
3. How would you manage this patient?
Answer
Answer
A 39 year old female presents with palpitations and collapse. Her BP on arrival is 95/55.
1. Describe the ECG, what is the diagnosis?
- Episode of broad complex tachycardia with alternating axis.
- Torsade de pointes
2. Give three possible causes
- Hypomagnesaemia
- Hypokalaemia
- Long QT syndrome congenital eg romano-ward, acquired eg TCA, quinidine, procainaide
- Brugada syndrome.
3. How would you manage this patient?
- Oxygen
- IVA – magnesium 2g IV 10 mins
- Treat underlying causes, if no improvement DC cardioversion
- Cardiology / Refer CCU.
Further read: Lifeinthefastlane
Causes of Prolonged QT syndrome:
- Genetic: Romano Ward, Lange Neilson
- Electrolytes: Hypokalaemia, hypomagnesaemia, hypocalcaemia
- Environmental: Hypothermia
- Drugs: Quinine, sotalol, amiodarone, organophosphates, antihistamines
- Cardiac: Myocarditis, IHD
- SAH
Chest Pain of Recent Onset Nice 2010:
- ECG asap
- O2- if sats <94% - aim for 94-98% unless at risk of hypercapnic respiratory failure
- Stable Angina unlikely if: continuous/prolonged; unrelated to activity; bought on by breathing in; association with dizziness, palpitations, tingling, swallow problem.
- Hx: chest pain radiating to both arms, with sweating and nausea lasting >15minutes
- Initial Trop T: if norm repeat 10-12 hrs
- Stable Angina: constricting; ppt by exertion; relieve <5mins by rest/GTN
CHADS2 - The CHADS2 score is a clinical prediction rule for estimating the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation.
- C Congestive heart failure 1
- H Hypertension: blood pressure consistently above 140/90 mmHg (or treated hypertension on medication) 1
- A Age ≥75 years 1
- D Diabetes mellitus 1
- S2 Prior Stroke or TIA or Thromboembolism 2
Score 0 aspirin; 1 aspirin or warfarin; 2 or more warfarin risk/benefit
The San Francisco Syncope Rule (SFSR) is a simple rule for evaluating the risk of adverse outcomes in patient who present with fainting or syncope. The mnemonic for features of the rule is CHESS (or CHEST):
- C - History of congestive heart failure
- H - Hematocrit < 30%
- E - Abnormal ECG
- S - Shortness of breath
- S - Triage systolic blood pressure < 90 A patient with any of the above measures is considered at high risk for a serious outcome SFSR has a sensitivity of 74-98% and specificity of 56%
Anti-ischaemic agents:
Beta-blockers:
- Effects on beta-1 receptors that decrease in myocardial oxygen consumption.
- The target heart rate for a good treatment effect should be between 50 and 60 eat per minute.
- Significantly impaired AV conduction and history of asthma or of acute LV dysfunction should NOT receive beta-blockers.
Nitrates:
- Venodilator leads to decrease pre-load and LV end-diastolic volume, resulting in a decrease in myocardial oxygen consumption. Titrated upwards until symptoms are relieved unless side effects occur.
Recommendations for anticoagulation:
- Fondaparinux is recommended on the basis of the most favourable efficacy/safety profile
- Enoxaparin has less favourable efficacy/safety profile than fondaparinux should be used if the bleeding risk is low.
- Aspirin irreversibly inhibits COX-1 in platelets, thereby limiting the formation of thromboxane A2, thus inhibiting platelet aggregation.
Non Cardiac conditions with troponin elevations:
- CCF
- Aortic dissection, aortic valve disease, or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Cardiac contusions, ablation, pacing, cardioversion
- Inflammatory diseases, e.g. myocarditis
- Pulmonary embolism, severe pulmonary hypertension
- Chronic or acute renal dysfunction
- Acute neurological disease, including stroke or SAH
- Drug toxicity
- Burns, if affecting >30% of body surface area
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Critically ill patients, especially with respiratory failure, or sepsis
Relevant Videos
Relevant Videos
Cardiology - Short Answer Questions (SAQ)

This is a brilliant blog! I'm very happy with the comments!.. best cancer doctors in Hyderabad
ReplyDelete